The importance of image segmentation for vegetation analysis
Why is so important image segmentation?
When the main goal is vegetation analysis, image segmentation is not only important, it is essential!
Explanation is very simple, in remote sensing the key aspect of an image is not the colors, but the data. Each pixel contains a numerical information for each one of the bands that compose the image, and that information is the base of the work that allows applying different algorithms. Whether a RGB, thermal, multispectral or hyperspectral sensor, pixel information is a measure of the mean spectral response of all the elements within that pixel. Obviously, the bigger pixel size (lower image resolution), the higher number of elements that could influence its spectral values.
The key advantage of very high-resolution images is that we are able to extract pure vegetation pixels, that is, pixels whose information corresponds exclusively to the spectral response of vegetation. Considering the entire scene (mosaic) we will also find information about soil pixels and about any other element located in the scene. Moreover, as it can be seen in the following image (corresponding to crop lines), in addition to the pure vegetation and soil pixels, the boundary between both components contain spectral information that is a mixed between the values corresponding to vegetation and the values corresponding to soil.
What happen if image segmentation is not conducted?
Comparing the spectra of each one of the three pixels highlighted in the previous image, it can be seen clearly the differences in the following graph. In the case of the pure vegetation pixel, as expected, the spectral signature has a perfect pattern. The same happens to the pure soil pixel, the spectral signature follows the expected pattern. However, the pixel located in the edge of the row, the spectral signature has influence of both covers. Therefore, if considering that kind of pixels for vegetation analysis the obtained results could not be fully representative.
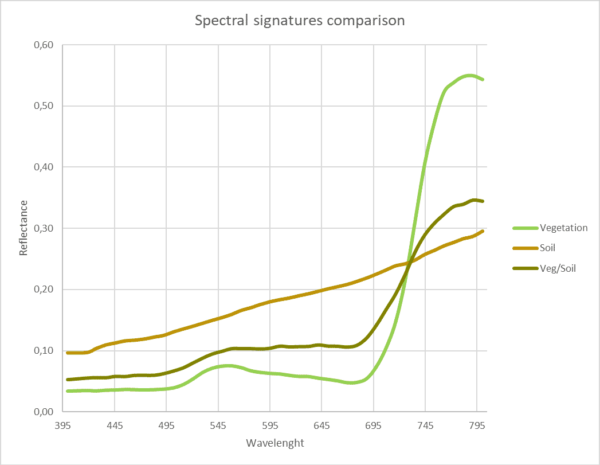
It is well known that for vegetation analysis we apply different algorithms (vegetation indices), which are mathematical operations with reflectance values in specific wavelengths. Each index uses values of some wavelengths or others according to the objective of the analysis (photosynthetic capacity, response of certain nutritional pigments, etc.).
If the values used to calculate these indices do not correspond with pure vegetation values, the calculation will be wrong and, therefore, the conclusions will not be valid.
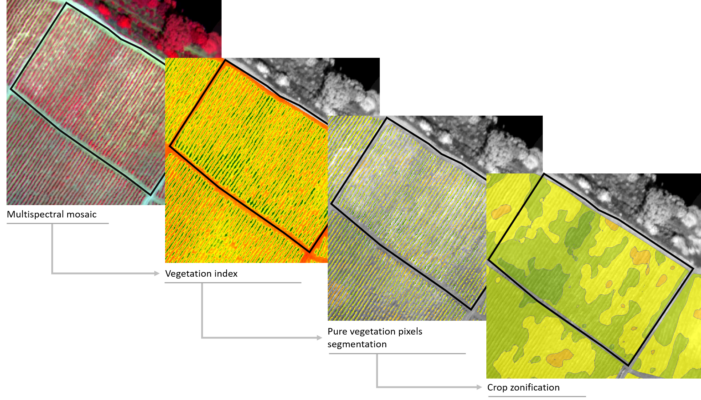
Next, the process for the characterization and analysis of a crop is shown, in which the final result is achieved from the segmentation of the pure vegetation pixels.
And the most important issue … How are the data affected if the image segmentation is not conducted?
As we already know, in remote sensing the key aspect is not the colors but the actual data, so let´s see how image segmentation affects the quality of results.
To check it out, in the hyperspectral sample image, 10 plots have been identified and a basic structural vegetation index (NDVI) was calculated for each plot over segmented and non-segmented mosaic.

It can be clearly observed that NDVI differs from segmented and non-segmented analysis. In general, NDVI values of segmented image are higher than non-segmented, since NDVI of soil is much lower than NDVI of vegetation (soil influence decreases NDVI values). Therefore, if image segmentation is not conducted, the NDVI values are wrong and they do not represent the reality.
It can be clearly observed that NDVI differs from segmented and non-segmented analysis. In general, NDVI values of segmented image are higher than non-segmented, since NDVI of soil is much lower than NDVI of vegetation (soil influence decreases NDVI values). Therefore, if image segmentation is not conducted, the NDVI values are wrong and they do not represent the reality.
Conclusions
Conducting vegetation analysis without a proper image segmentation of pure vegetation pixels is a critical mistake. It does not matter that we use a last generation sensor with high spectral and geometric quality, if image processing is not properly performed, because we will be making a large errors that will spoil the quality of the data.



